7-ZIP command line tool version, 7z.exe, allows you to execute commands using the system terminal. 7-Zip is a powerful, open-source, and user-friendly program that offers support for most file archives like 7z, ZIP, RAR, TAR, and GZIp, among others. These characteristics make 7-Zip easy to download and be used for personal or commercial purposes.
By using the command-line version, you can access all features from the terminal even without a Graphical User Interface (GUI). Before we discuss any further about the different commands for 7-Zip, check out 7-Zip for more of our helpful guides.
For a Mac computer running macOS Catalina or later releases, the default Unix Shell is Zsh. Your default shell is available via the Terminal program within your Utilities folder. To open Terminal, try one or both of the following: In Finder, select the Go menu, then select Utilities. Locate Terminal in the Utilities folder and open it. 7-ZIP command line tool version, 7z.exe, allows you to execute commands using the system terminal. 7-Zip is a powerful, open-source, and user-friendly program that offers support for most file archives like 7z, ZIP, RAR, TAR, and GZIp, among others. These characteristics make 7-Zip easy to download and be used for personal or commercial purposes.
Which is the best tool, 7-Zip vs WinRAR? Is 7Zip safe? These are some of the questions that you should also clarify before learning how to use 7Zip. You also need to understand the issues with 7-Zip cannot open file as archive that the tool sometimes experiences.
7-Zip can be used to compress, extract, test run-list, add, and update archive files. The 7z.exe version works with Windows, while 7-Zip is the command-line version for Linux, Mac OS X, and UNIX. The 7z format has several main features that include open architecture, high ratio, and secure AES – 256 encryption options. This software lets you use any compression or encryption method. The format supports file sizes of up to 16000000GB and Unicode file names. In the next section, we’ll be showing you some of the common commands that are used with this software.
Contents
- 9 Switches
- 9.1 Frequently Asked Questions
Command Examples for Windows
The 7-Zip command-line executable file is the 7za.exe. You can use the EXE file to run commands on archives. In our examples, we’ll be using “C:UsersName” as our user directory. Below is a step-by-step guide to getting you started on the command line:
- Before proceeding to other commands, one helpful tip is to place 7za.exe in your directory. This will give you convenience since you won’t have to change the environment paths.
- Launch the Windows console and test the 7za.exe program out using a few commands
- Type in the exe name, 7za, to display the file details
On the command line, the default command and output looks like this:
7za <command> [<switches>…] <archive_name>
[<file_names>…]
[<@listfiles…>]
Before we proceed with our examples, check out other guides, and reviews on our website. You might be interested in our 7-Zip vs WinRAR review and our 7-Zip password protect guide.
Function Letter Command
In this section, we’re going walk you through function letter commands. Because they are only single letters, they are quite easy to memorize.
Aside from looking for the details about 7-Zip download for PC or for Linux, it is important to have idea about archive error. Because the command line is useless if you don’t know how to fix 7-Zip cannot open file.
Archive and Add to ZIP
The function letter a command is used to put data in the archives. This “a” command stands for “archive” or “add.” To do this successfully, you must specify the archive location and the source files. Using the command will look like this on the terminal line:
C:UsersName>7za a -t7z files.7z *.txt
7-Zip (A) 4.60 beta Copyright (c) 1999-2008 Igor Pavlov 2008-08-19
Scanning
Creating archive files.7z
Compressing fileA.txt
Compressing fileB.txt
Everything is Ok
C:UsersName>
Delete
The function letter d command is used for removing a particular file or files from an archive. This “d” command stands for delete. Using the command will look like this on the terminal line:
7z d example.zip *.bak -r
Let’s break down the command so you won’t get confused. The command stands for the following:
7z: use the executable file
d: delete files
example.zip: delete from this archive
*.bak: only match bak files
-r: traverse all subdirectories
Extract and Enlarge
The function letter e command is useful when there is no substantial archive. The “e” command stands for extract to unzip or enlarge and archive. Using the command will look like this on the terminal line:
7z e example.zip
Again, let’s break it down to help you understand. In this command, we see the following words/commands:
7z: use the executable file
e: use the extract command
example.zip: the source archive you are expanding
Meanwhile, the function letter x command works the same way with e. The difference is it preserves the full paths. This is useful if you have an elaborate or important directory structure. Also, this is useful for backups. Using the command on the terminal looks like this:
7z x example.zip
In this command, we see the following words/commands:
7z: use the executable file
x: use the extract command
example.zip: the archive where you want to extract all the files from
List

This function letter lowercase L command is used to list the archive contents. The “l” command stands for list. However, you may not need to use this command it often. Using the command on the terminal looks like this:
C:UsersName>7za l files.7z
Test
This function letter t command is used to test the integrity of archives. The “t” command stands for test. However, this is much less useful than the “-t” switch. Using the command on the terminal looks like this:
7z t example.zip *doc -r
In this command, we see the following words/commands:
7z: use the executable file
t: test the specific archive
example.zip: the archive to be tested
*.doc: test all the doc files in the archive
-r: recurse all the child directories
Update
This function letter u command is used to replace old files in your archive with newer files. The “u” command stands for update. This command prevents needing to decompress and recompress the entire archive. This command will not work with solid archives. Using the command on the terminal looks like this:
7z u example.zip *.doc
We see the following words/commands:
7z: use the executable file
u: update command
example.zip: the archive you want to update files in
*.doc: only update the doc files
Switches
Another command that we see on the command line is the switch. The switch is composed of a switch specifier and the name of the switch. The specifier is either a dash (-) or a forward slash (/). Switches often look like this:
Below is a list of common switches:
Frequently Asked Questions
 📡 How to use the 7-Zip command line?
📡 How to use the 7-Zip command line? 
Launch window and run the version of 7-Zip you are using by entering “7z” for P7Zip (7z.exe), or “7za” for 7-Zip in Windows (7za.exe) to either run the P7-Zip or 7za application before you enter commands. After that, you can use any of the commands listed above. Make sure that you’re following the syntax when typing in your commands.
💡 How to extract with 7-Zip command line?You can use the e or x commands to extract ZIP files.
📁 How to create a 7-Zip file command line?Use the “a” command to create a new archive file which can end in 7z, XZ, GZIP, TAR, ZIP, and many more.
📦 How to zip a file using 7-Zip command line?Use the “a” command to add files to the ZIP file.
7-Zip Command Line: Conclusion
Even without a GUI, you can use all the features of 7Zip on the command line. Just as long as you familiarize yourself with some of the commands, you’ll get better with practice. Did we miss any commands on our list? Let us know by leaving us a message in the comment section below.
 7zip command line
7zip command lineDownload files
You need to download some files to follow this lesson.
- Download data-shell.zip and move the file to your Desktop.
- Unzip/extract the file.Let your instructor know if you need help with this step.You should end up with a new folder called
data-shellon your Desktop.
Install software
If you do not already have the shell software installed, you will need todownload and install it.
Open a new shell
After installing the software
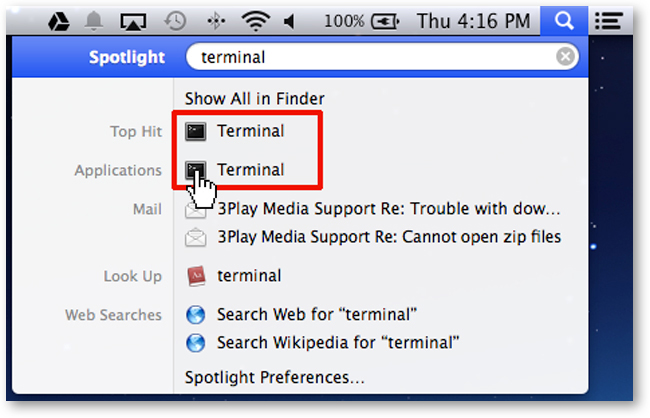
- Open a terminal.If you’re not sure how to open a terminal on your operating system, see the instructions below.
- In the terminal type
cdthen press the Return key.This step will make sure you start with your home folder as your working directory.
In the lesson, you will find out how to access the data files in this folder.
Where to type commands: How to open a new shell
The shell is a program that enables us to send commands to the computer and receive output.It is also referred to as the terminal or command line.
Some computers include a default Unix Shell program.The steps below describe some methods for identifying and openinga Unix Shell program if you already have one installed.There are also options for identifying and downloading a Unix Shell program,a Linux/UNIX emulator, or a program to access a Unix Shell on a server.
If none of the options below address your circumstances,try an online search for: Unix shell [your computer model] [your operating system].
Computers with Windows operating systems do not automatically have a Unix Shell programinstalled.In this lesson, we encourage you to use an emulator included in Git for Windows,which gives you access to both Bash shell commands and Git.
Unzip Mac Terminal Command Linux
Once installed, you can open a terminal by running the program Git Bash from the Windows startmenu.
For advanced users:
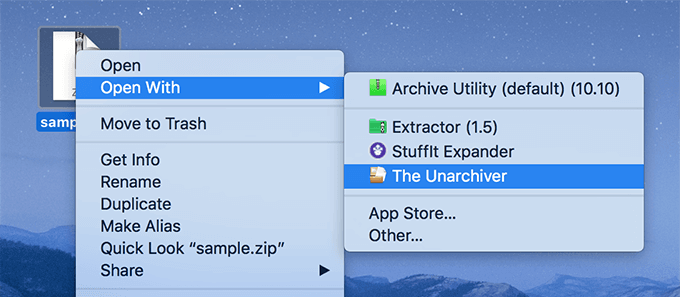
Unzip Mac Terminal Commands
As an alternative to Git for Windows you may wish to Install the Windows Subsystem for Linuxwhich gives access to a Bash shell command-line tool in Windows 10.
Unzip Mac Terminal Command Cmd
Please note that commands in the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) may differ slightlyfrom those shown in the lesson or presented in the workshop.
